





Transcript
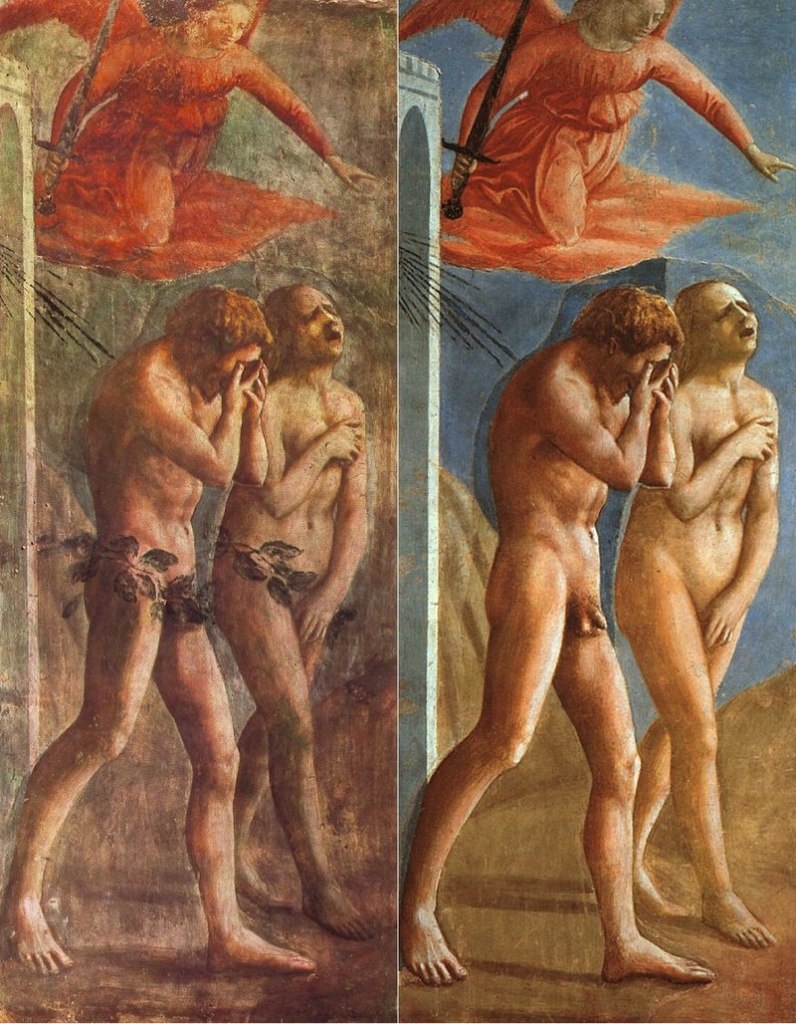
Something about history that usually remains true is that very few people are ever aware of the significance of the times they live through. The Romans of their late fourth century CE didn’t know their children and grandchildren would be the last citizens of the empire nor did the Prophet Muhammad’s contemporaries realize their compatriots would crush the superpowers of their day, the Eastern Roman and Sassanid Empires, and start a religion that would change the world. And no one ever thought of themselves as living through the colonial era or the Enlightenment or whathaveyou. If any generations ever knew exactly what era they were living through, it was the people who lived to see the Renaissance. While it was a nineteenth century historian, Jules Michelet, who did first slap the label “Renaissance” on the whole period, it really was Giorgio Vasari, the humanist who wrote Lives of the Most Excellent Painters, Sculptors, and Architects, who coined the metaphor of “rebirth” when referring to the accomplishments of the artists he described in his work.

